Boost your energy, and restore your vitality – NMN and NR are your keys to a longer, healthier life.
At askdoctor.ai, discover the science-backed benefits of NMN and NR, two powerful longevity supplements designed to enhance the body and cognitive function. This guide combines the knowledge, benefits, side effects, dosages, and real-life stories of those who took these supplements. We are here to support you with knowledge, and strategies.
What Are NMN and NR? The Science-Backed Longevity Supplements Everyone’s Talking About
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a small molecule that helps the body produce NAD⁺, an important substance needed for energy, repairing DNA, and controlling how genes work.
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a type of vitamin B₃ that helps the body make NAD⁺, a key molecule needed for energy, repairing DNA, and controlling how genes work.
Both NMN & NR have the same functions in the body but are different in their process and chemical structure. Here we will discuss this in detail.
What is NMN: How it works
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a molecule that plays a crucial role in the production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺), a vital compound found in all living cells. NAD⁺ is essential for various biological functions, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation.
How NMN Works in the Body:
As a precursor to NAD⁺, NMN contributes to increasing NAD⁺ levels within cells. When you consume NMN, your body absorbs and converts it into NAD⁺ through a series of enzymatic reactions. This elevation in NAD⁺ levels supports several critical cellular processes such as:
- Energy Production: NAD⁺ is integral to cellular respiration, facilitating the conversion of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell.
- DNA Repair: NAD⁺ activates enzymes like PARPs, which detect and repair damaged DNA, thereby maintaining genomic stability.
- Gene Expression Regulation: NAD⁺ influences the activity of sirtuins, a family of proteins that regulate gene expression related to aging and metabolism.
Health Benefits of NMN:
Research, primarily in animal models, suggests that NMN supplementation may offer several health benefits:
- Metabolic Enhancement: Studies in mice have shown that NMN supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity and mitigate age-associated weight gain.
- Cardiovascular Health: Researchers have observed that NMN promotes a healthier expression profile of microRNAs in the aorta of aged mice, which may predict anti-atherogenic effects.
- Neuroprotection: Animal studies indicate that NMN may have neuroprotective effects, potentially benefiting cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Side Effects of NMN
It’s important to note that while NMN is related to other forms of vitamin B3, such as nicotinamide and nicotinic acid, their side effect profiles may differ. For instance, nicotinamide has minimal side effects, with liver toxicity documented at very high doses above 3 grams per day. Nicotinic acid, on the other hand, can cause flushing and, at doses greater than 2 grams per day, has been associated with liver damage.
Given the limited research on NMN’s side effects, especially with long-term use, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting NMN supplementation.
Dosages of NMN
A study conducted at Keio University in Japan found that a single oral dose of up to 500 mg of NMN was safe in healthy men. However, comprehensive data on the optimal dosage, efficacy, and long-term safety of NMN supplementation in humans remain scarce.
Given the current state of research, there is no universally recommended dosage for NMN supplementation. If you are considering taking NMN, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss potential benefits and risks based on your health profile.
Human Clinical Trials and Safety:
Human studies on NMN are ongoing. Preliminary clinical trials have demonstrated that NMN supplementation increases blood NAD⁺ concentrations and is safe and well-tolerated at doses up to 900 mg daily.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a molecule that serves as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺), a coenzyme essential for various biological processes, including energy metabolism and DNA repair. While NMN is naturally present in certain foods, the concentrations are relatively low.
Natural Dietary Sources of NMN:
- Vegetables:
- Broccoli: Contains approximately 0.25 to 1.12 mg of NMN per 100 grams.
- Cabbage: Offers up to 0.9 mg per 100 grams.
- Edamame (young soybeans): Known to have NMN content, though specific amounts may vary.
- Cucumbers and Avocados: Also contribute small amounts of NMN to the diet.
- Fruits:
- Tomatoes: Provide about 0.26 to 0.30 mg per 100 grams.
- Animal Products:
- Raw Beef: Contains between 0.06 to 0.42 mg per 100 grams.
It’s important to note that while these foods do contain NMN, the amounts are relatively modest. For instance, consuming 100 grams of broccoli may provide up to 1.12 mg of NMN, which is significantly lower than the doses typically used in research studies exploring NMN’s health benefits. Therefore, obtaining therapeutic levels of NMN solely through diet would be challenging.

Image by healthaidealways from Pixabay
What is NR: How it works
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B₃ that serves as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺), a crucial coenzyme involved in numerous metabolic processes within the body. NAD⁺ plays a pivotal role in energy production, DNA repair, and the regulation of gene expression.
Mechanism of Action:
Upon ingestion, the bloodstream absorbs NR and transports it to cells throughout the body. Inside the cells, NR undergoes phosphorylation by nicotinamide riboside kinases (NRK1 and NRK2) to form nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Subsequently, NMN adenylyl transferases convert NMN into NAD⁺. This pathway effectively elevates intracellular NAD⁺ levels, which is essential for various cellular functions.
Physiological Roles of NAD⁺:
- Energy Metabolism: NAD⁺ is central to cellular respiration, facilitating the conversion of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell.
- DNA Repair: NAD⁺ serves as a substrate for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), enzymes involved in detecting and repairing DNA damage, thereby maintaining genomic stability.
- Gene Expression Regulation: NAD⁺ influences the activity of sirtuins, a family of proteins that regulate gene expression related to aging and metabolism.
Health Benefits of NR:
Research into NR supplementation has revealed several potential health benefits:
- Metabolic Health: Studies indicate that NR supplementation can enhance mitochondrial function and improve metabolic parameters, potentially offering protection against metabolic disorders.
- Neuroprotection: Elevated NAD⁺ levels through NR supplementation have shown protective effects against neurodegenerative conditions in preclinical models.
- Muscle Function: In human studies, researchers have associated NR supplementation with improved muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and satellite cell differentiation, suggesting benefits for muscle health.
Side Effects of NR
As of now, specific information regarding the side effects of NR is limited and not comprehensively detailed in available sources, including Wikipedia. However, it’s noteworthy that other forms of vitamin B₃, such as nicotinic acid and nicotinamide, have documented side effects at high doses. For instance, nicotinic acid can cause flushing and, at doses greater than 2 grams per day, has been associated with liver damage. Nicotinamide has minimal side effects, though liver toxicity has been observed at very high doses above 3 grams per day.
Dosages of NR
Common Dosage Recommendations:
- General Wellness: A typical dosage ranges from 250 to 500 milligrams per day.
- Specific Health Objectives: Some studies have explored higher doses. For instance, research involving healthy volunteers administered up to 1,000 mg of NR twice daily (totaling 2,000 mg per day) without significant adverse effects.
Safety and Tolerability:
NR supplementation is generally well-tolerated. A study reported that a daily intake of 3,000 mg over four weeks was well-tolerated without moderate or severe adverse events. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as nausea, bloating, or skin issues like itching and sweating.
Considerations:
- Consult Healthcare Professionals: Before starting NR supplementation, especially at higher doses, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and appropriateness for your individual health circumstances.
- Product Quality: Ensure that the NR supplement is sourced from reputable manufacturers that adhere to quality standards and have undergone third-party testing.
Safety and Regulatory Status:
Regulatory authorities generally recognize NR as safe for consumption, and clinical trials have demonstrated its safety and tolerability in humans. However, as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before initiating NR supplementation.
Certain foods, primarily those rich in vitamin B3, naturally contain small amounts of nicotinamide riboside (NR). Some of the best dietary sources of NR include:
Natural Dietary Sources of NR:
- Milk & Dairy Products – Cow’s milk is one of the richest natural sources of NR.
- Fish – Salmon and tuna contain NR and other NAD⁺ precursors.
- Meat – Chicken, beef, and pork provide NR along with other forms of vitamin B3.
- Mushrooms – Particularly cremini and portobello mushrooms.
- Yeast – Brewer’s yeast and nutritional yeast contain NR.
- Whole Grains – Brown rice, whole wheat, and barley have small amounts.
- Vegetables – Broccoli, cabbage, and avocados provide NR but in lower amounts.

Image from Stockcake
NR in the Diet vs. Supplements
For Diet
- Natural Sources: Foods like milk, yeast, and certain vegetables contain small amounts of NR. However, the quantities are relatively low, so getting a significant amount through diet alone can be challenging.
- Absorption: The body may convert other forms of B3 (like nicotinic acid) into NR, but this process occurs more slowly than taking a supplement directly.
- Long-Term Effects: Eating foods rich in NR is generally safe, and these foods also provide other nutrients beneficial for overall health. However, there may not be enough NR in food to achieve the higher doses seen in supplement studies.
For Supplements
- Higher Doses: Supplements can deliver higher, more concentrated doses of NR. Studies suggest that higher NR doses can have more significant effects on mitochondrial health and aging-related biomarkers.
- Bioavailability: Manufacturers design NR supplements to be highly bioavailable, meaning the body absorbs and utilizes them more easily than food sources.
- Effectiveness: Some research supports the idea that NR supplements may help increase NAD+ levels, which is important for cellular energy and repair processes. However, researchers have still gathered limited long-term data.
Conclusion
- Diet: It’s a natural and safer way to get NR, though the levels may not be high enough to see potential therapeutic benefits.
- Supplements: They can provide more targeted and higher doses, potentially yielding more pronounced effects, but they might not always be necessary for general health if you have a balanced diet.
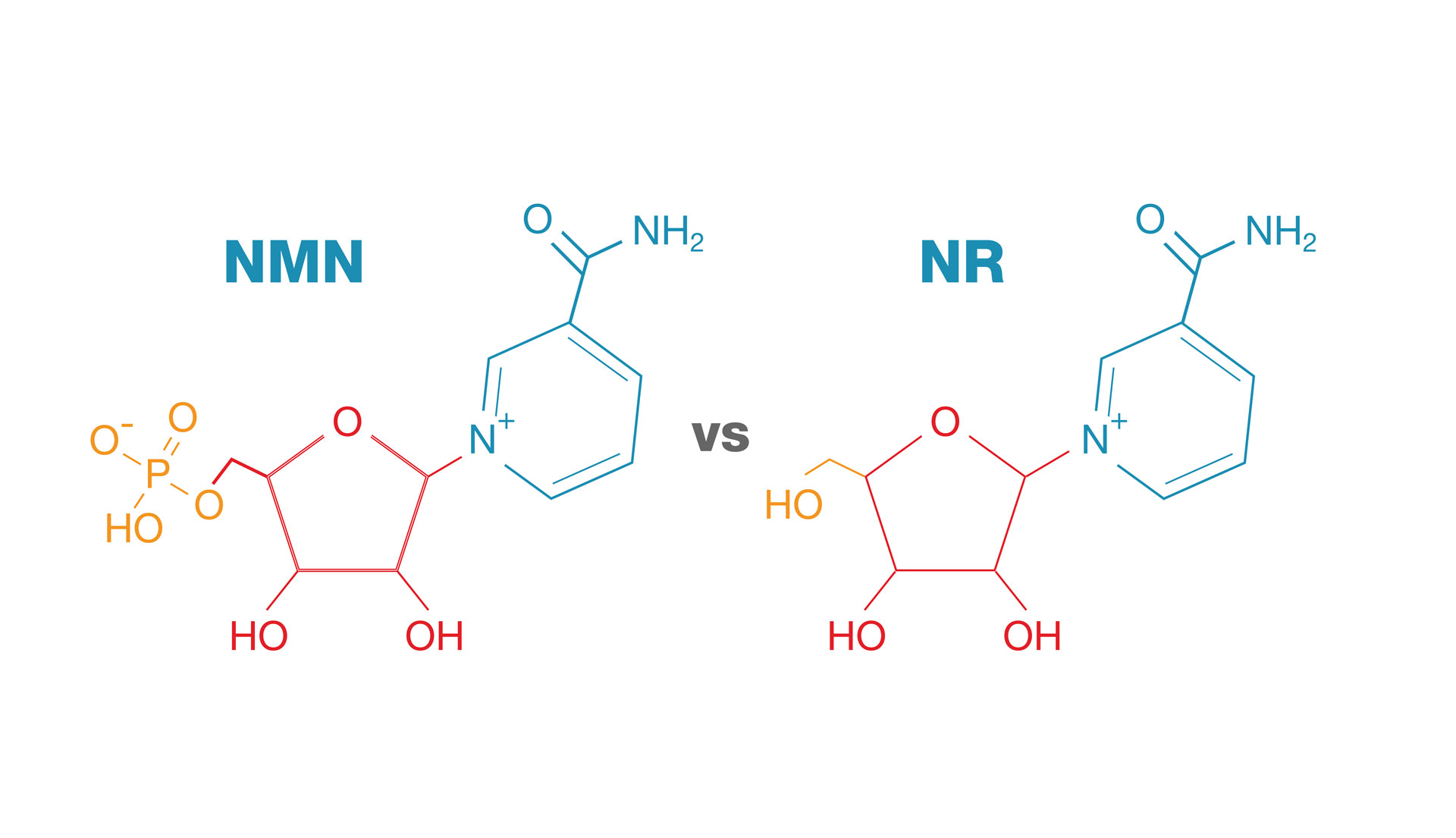
Difference Between the NMN & NR
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) are both precursors to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+), a vital coenzyme involved in numerous cellular processes, including metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation. As NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, supplementing with its precursors like NMN and NR has garnered attention for potential anti-aging and health benefits.
Chemical Structure and Conversion Pathways:
- NMN: NMN derives from ribose and nicotinamide. In mammals, cells synthesize NMN from nicotinamide through the salvage pathway, where nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (NAMPT) catalyzes its formation. Once cells produce NMN, the enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase (NMNAT) converts it into NAD⁺.
- NR: NR is a form of vitamin B₃ and serves as a precursor to NAD+ through a distinct pathway. Once inside the cell, nicotinamide riboside kinases (NRK1 and NRK2) phosphorylate NR to form NMN, and NMNAT subsequently converts it into NAD⁺. This pathway bypasses the NAMPT-mediated step, potentially offering an alternative route for NAD+ biosynthesis.
Research and Potential Benefits:
Animal studies have demonstrated that supplementation with either NMN or NR can increase NAD+ levels, leading to improved mitochondrial function, enhanced energy metabolism, and potential neuroprotective effects. For instance, research in mice has shown that NMN supplementation ameliorates age-associated physiological decline by boosting NAD+ levels. Similarly, researchers have identified NR as an NAD precursor involved in NAD⁺ synthesis in both bacteria and eukaryotes.
| Features | NMN | NR |
| Longevity & Anti-Aging | Strong potential | Strong potential |
| Brain Function & Cognitive Support | May protect against neurodegeneration | Enhances brain energy metabolism |
| Metabolic Health (Weight, Blood Sugar) | Supports glucose metabolism | May improve insulin sensitivity |
| Muscle Endurance & Recovery | Stronger effects in animal studies | Beneficial but less studied |
| Heart Health | Improves vascular function | Supports cardiovascular health |
NMN vs. NR: Which is Better?
Both NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) and NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) are precursors to NAD⁺, an essential molecule for energy production, DNA repair, and overall cellular health. However, they have some differences in absorption, efficiency, and research backing.
Comparison of NMN and NR
Absorption & Conversion
- The body converts NR into NMN before transforming it into NAD⁺, adding an extra step.
- The body directly converts NMN into NAD⁺, making it potentially more efficient.
Scientific Research
- NR has been studied longer and has more human clinical trials.
- NMN research is growing rapidly, with promising results in animal and early human studies.
Bioavailability & Effectiveness
- The body absorbs NR quickly but may not raise NAD⁺ levels as effectively as NMN.
- Cells can directly use NMN, which may provide a faster NAD⁺ boost.
Longevity & Anti-Aging Benefits
- Both NMN and NR support healthy aging, but NMN may have a slight edge in activating longevity-related pathways.
Price & Availability
- NR is more widely available and often more affordable.
- NMN is newer and can be more expensive but is gaining popularity.
NMN Vs NR: Which One is Better?
- If you want a more direct NAD⁺ booster: NMN may be better.
- If you prefer a well-researched, cost-effective option: NR is a good choice.
- For longevity & anti-aging effects: NMN has a slight advantage.
Real-Life Success Stories Who Get Benefits from NMN & NR
If you’re taking NMN or NR, you’re investing in your health, energy, and longevity. These powerful molecules are helping people around the world feel more energetic, youthful, and resilient—and you are part of that journey!
Everyday, countless individuals report:
- More energy and reduced fatigue
- Sharper memory and better focus
- Faster recovery from exercise
- Healthier aging with fewer aches and pain
- Stronger cells for long-term wellness
Science is making incredible progress in cellular health and longevity, and you are on the cutting edge of this transformation. Keep going, stay consistent, and trust the process—your body is working behind the scenes to create a healthier, more vibrant you! Here we will share real-life stories.
Jesse Coomer Success Stories: He Took NMN for 100 Days and This Happened
Shock NAD results after 11-month NMN trial
Richard: NMN Trial 1 Year Result
NMN 12-month report of physical appearance changes. His wife and he have been taking NMN supplements for one year now after they heard the talks of Dr. David Sinclair. In this video we talk about the changes that have happened since they started taking NMN. Also, video clips for the past year!
Reference:
Wikipedia on NMN & NR
National Institute of Medicine on NMN & NR
Harvard on NMN & NR
Health Line on NMN & NR





Leave a Reply